Week 12 [Fri, Oct 29th] - Topics
Detailed Table of Contents
Guidance for the item(s) below:
Previously, you learned about equivalence partitions, a heuristic for dividing the possible test cases into partitions. But which test cases should we pick from each partition? Next, let us learn another heuristic which can addresses that problem.
Can explain boundary value analysis
Boundary Value Analysis (BVA) is a test case design heuristic that is based on the observation that bugs often result from incorrect handling of boundaries of equivalence partitions. This is not surprising, as the end points of boundaries are often used in branching instructions, etc., where the programmer can make mistakes.
The markCellAt(int x, int y) operation could contain code such as if (x > 0 && x <= (W-1)) which involves the boundaries of x’s equivalence partitions.
BVA suggests that when picking test inputs from an equivalence partition, values near boundaries (i.e. boundary values) are more likely to find bugs.
Boundary values are sometimes called corner cases.
Exercises
Can apply boundary value analysis
Typically, you should choose three values around the boundary to test: one value from the boundary, one value just below the boundary, and one value just above the boundary. The number of values to pick depends on other factors, such as the cost of each test case.
Some examples:
| Equivalence partition | Some possible test values (boundaries are in bold) |
|---|---|
[1-12] | 0,1,2, 11,12,13 |
[MIN_INT, 0] | MIN_INT, MIN_INT+1, -1, 0 , 1 |
[any non-null String] | Empty String, a String of maximum possible length |
[prime numbers] | No specific boundary |
[non-empty Stack] | Stack with: no elements, one element, two elements, no empty spaces, only one empty space |
Guidance for the item(s) below:
Earlier, you learned Equivalence Partitioning, Boundary Value Analysistwo heuristics that can improve the test case quality. Even when applying them, the number of test cases can increase when the SUT takes multiple inputs. Let's see how we can deal with such situations.
Can explain the need for strategies to combine test inputs
An SUT can take multiple inputs. You can select values for each input (using equivalence partitioning, boundary value analysis, or some other technique).
An SUT that takes multiple inputs and some values chosen for each input:
- Method to test:
calculateGrade(participation, projectGrade, isAbsent, examScore) - Values to test:
Input Valid values to test Invalid values to test participation 0, 1, 19, 20 21, 22 projectGrade A, B, C, D, F isAbsent true, false examScore 0, 1, 69, 70, 71, 72
Testing all possible combinations is effective but not efficient. If you test all possible combinations for the above example, you need to test 6x5x2x6=360 cases. Doing so has a higher chance of discovering bugs (i.e. effective) but the number of test cases will be too high (i.e. not efficient). Therefore, you need smarter ways to combine test inputs that are both effective and efficient.
Quality Assurance → Test Case Design → Combining Test Inputs → Test input combination strategies
Can explain some basic test input combination strategies
Given below are some basic strategies for generating a set of test cases by combining multiple test inputs.
Let's assume the SUT has the following three inputs and you have selected the given values for testing:
SUT: foo(char p1, int p2, boolean p3)
Values to test:
| Input | Values |
|---|---|
| p1 | a, b, c |
| p2 | 1, 2, 3 |
| p3 | T, F |
The all combinations strategy generates test cases for each unique combination of test inputs.
This strategy generates 3x3x2=18 test cases.
| Test Case | p1 | p2 | p3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | 1 | T |
| 2 | a | 1 | F |
| 3 | a | 2 | T |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 18 | c | 3 | F |
The at least once strategy includes each test input at least once.
This strategy generates 3 test cases.
| Test Case | p1 | p2 | p3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | 1 | T |
| 2 | b | 2 | F |
| 3 | c | 3 | VV/IV |
VV/IV = Any Valid Value / Any Invalid Value
The all pairs strategy creates test cases so that for any given pair of inputs, all combinations between them are tested. It is based on the observation that a bug is rarely the result of more than two interacting factors. The resulting number of test cases is lower than the all combinations strategy, but higher than the at least once approach.
This strategy generates 9 test cases:
See steps
| Test Case | p1 | p2 | p3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | 1 | T |
| 2 | a | 2 | T |
| 3 | a | 3 | F |
| 4 | b | 1 | F |
| 5 | b | 2 | T |
| 6 | b | 3 | F |
| 7 | c | 1 | T |
| 8 | c | 2 | F |
| 9 | c | 3 | T |
A variation of this strategy is to test all pairs of inputs but only for inputs that could influence each other.
Testing all pairs between p1 and p3 only while ensuring all p2 values are tested at least once:
| Test Case | p1 | p2 | p3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | 1 | T |
| 2 | a | 2 | F |
| 3 | b | 3 | T |
| 4 | b | VV/IV | F |
| 5 | c | VV/IV | T |
| 6 | c | VV/IV | F |
The random strategy generates test cases using one of the other strategies and then picks a subset randomly (presumably because the original set of test cases is too big).
There are other strategies that can be used too.
Guidance for the item(s) below:
Testing is the first thing that comes to mind when you hear 'Quality Assurance' but there are other QA techniques that can complement testing. Let's first take a step back and take a look at QA in general, followed by a look at some other QA techniques.
Can explain software quality assurance
Software Quality Assurance (QA) is the process of ensuring that the software being built has the required levels of quality.
While testing is the most common activity used in QA, there are other complementary techniques such as static analysis, code reviews, and formal verification.
Can explain validation and verification
Quality Assurance = Validation + Verification
QA involves checking two aspects:
- Validation: are you building the right system i.e., are the requirements correct?
- Verification: are you building the system right i.e., are the requirements implemented correctly?
Whether something belongs under validation or verification is not that important. What is more important is that both are done, instead of limiting to only verification (i.e., remember that the requirements can be wrong too).
Exercises
Can explain code reviews
Code review is the systematic examination of code with the intention of finding where the code can be improved.
Reviews can be done in various forms. Some examples below:
Pull Request reviews
- Project Management Platforms such as GitHub and BitBucket allow the new code to be proposed as Pull Requests and provide the ability for others to review the code in the PR.
In pair programming
- As pair programming involves two programmers working on the same code at the same time, there is an implicit review of the code by the other member of the pair.
Formal inspections
Inspections involve a group of people systematically examining project artifacts to discover defects. Members of the inspection team play various roles during the process, such as:
- the author - the creator of the artifact
- the moderator - the planner and executor of the inspection meeting
- the secretary - the recorder of the findings of the inspection
- the inspector/reviewer - the one who inspects/reviews the artifact
Advantages of code review over testing:
- It can detect functionality defects as well as other problems such as coding standard violations.
- It can verify non-code artifacts and incomplete code.
- It does not require test drivers or stubs.
Disadvantages:
- It is a manual process and therefore, error prone.
Resources
- 10 tips for reviewing code you don’t like - a blog post by David Lloyd (a Red Hat developer).
Can explain static analysis
Static analysis: Static analysis is the analysis of code without actually executing the code.
Static analysis of code can find useful information such as unused variables, unhandled exceptions, style errors, and statistics. Most modern IDEs come with some inbuilt static analysis capabilities. For example, an IDE can highlight unused variables as you type the code into the editor.
The term static in static analysis refers to the fact that the code is analyzed without executing the code. In contrast, dynamic analysis requires the code to be executed to gather additional information about the code e.g., performance characteristics.
Higher-end static analysis tools (static analyzers) can perform more complex analysis such as locating potential bugs, memory leaks, inefficient code structures, etc.
Some example static analyzers for Java: CheckStyle, PMD, FindBugs
Linters are a subset of static analyzers that specifically aim to locate areas where the code can be made 'cleaner'.
Can explain formal verification
Formal verification uses mathematical techniques to prove the correctness of a program.
An introduction to Formal Methods
Advantages:
- Formal verification can be used to prove the absence of errors. In contrast, testing can only prove the presence of errors, not their absence.
Disadvantages:
- It only proves the compliance with the specification, but not the actual utility of the software.
- It requires highly specialized notations and knowledge which makes it an expensive technique to administer. Therefore, formal verifications are more commonly used in safety-critical software such as flight control systems.
Exercises
Guidance for the item(s) below:
In a previous week, you learned about sequential and iterative ways of doing a software. Now, let us take a quick look at a couple of well-known processes used in the industry, both of which fall into a category called agile processes.
Can explain agile process models
In 2001, a group of prominent software engineering practitioners met and brainstormed for an alternative to documentation-driven, heavyweight software development processes that were used in most large projects at the time. This resulted in something called the agile manifesto (a vision statement of what they were looking to do).
You are uncovering better ways of developing software by doing it and helping others do it.
Through this work you have come to value:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
That is, while there is value in the items on the right, you value the items on the left more.
-- Extract from the Agile Manifesto
Subsequently, some of the signatories of the manifesto went on to create process models that try to follow it. These processes are collectively called agile processes. Some of the key features of agile approaches are:
- Requirements are prioritized based on the needs of the user, are clarified regularly (at times almost on a daily basis) with the entire project team, and are factored into the development schedule as appropriate.
- Instead of doing a very elaborate and detailed design and a project plan for the whole project, the team works based on a rough project plan and a high level design that evolves as the project goes on.
- There is a strong emphasis on complete transparency and responsibility sharing among the team members. The team is responsible together for the delivery of the product. Team members are accountable, and regularly and openly share progress with each other and with the user.
There are a number of agile processes in the development world today. eXtreme Programming (XP) and Scrum are two of the well-known ones.
Exercises
Can explain scrum
This description of Scrum was adapted from Wikipedia [retrieved on 18/10/2011], emphasis added:
Scrum is a process skeleton that contains sets of practices and predefined roles. The main roles in Scrum are:
- The Scrum Master, who maintains the processes (typically in lieu of a project manager)
- The Product Owner, who represents the stakeholders and the business
- The Team, a cross-functional group who do the actual analysis, design, implementation, testing, etc.
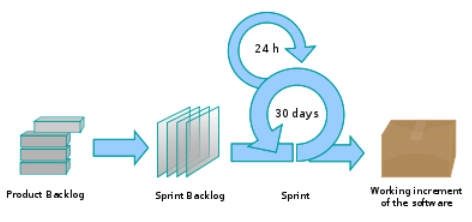
A Scrum project is divided into iterations called Sprints. A sprint is the basic unit of development in Scrum. Sprints tend to last between one week and one month, and are a timeboxed (i.e. restricted to a specific duration) effort of a constant length.
Each sprint is preceded by a planning meeting, where the tasks for the sprint are identified and an estimated commitment for the sprint goal is made, and followed by a review or retrospective meeting, where the progress is reviewed and lessons for the next sprint are identified.
During each sprint, the team creates a potentially deliverable product increment (for example, working and tested software). The set of features that go into a sprint come from the product backlog, which is a prioritized set of high level requirements of work to be done. Which backlog items go into the sprint is determined during the sprint planning meeting. During this meeting, the Product Owner informs the team of the items in the product backlog that he or she wants completed. The team then determines how much of this they can commit to complete during the next sprint, and records this in the sprint backlog. During a sprint, no one is allowed to change the sprint backlog, which means that the requirements are frozen for that sprint. Development is timeboxed such that the sprint must end on time; if requirements are not completed for any reason they are left out and returned to the product backlog. After a sprint is completed, the team demonstrates the use of the software.
Scrum enables the creation of self-organizing teams by encouraging co-location of all team members, and verbal communication between all team members and disciplines in the project.
A key principle of Scrum is its recognition that during a project the customers can change their minds about what they want and need (often called requirements churn), and that unpredicted challenges cannot be easily addressed in a traditional predictive or planned manner. As such, Scrum adopts an empirical approach—accepting that the problem cannot be fully understood or defined, focusing instead on maximizing the team’s ability to deliver quickly and respond to emerging requirements.
Daily Scrum is another key scrum practice. The description below was adapted from https://www.mountaingoatsoftware.com (emphasis added):
In Scrum, on each day of a sprint, the team holds a daily scrum meeting called the "daily scrum.” Meetings are typically held in the same location and at the same time each day. Ideally, a daily scrum meeting is held in the morning, as it helps set the context for the coming day's work. These scrum meetings are strictly time-boxed to 15 minutes. This keeps the discussion brisk but relevant.
...
During the daily scrum, each team member answers the following three questions:
- What did you do yesterday?
- What will you do today?
- Are there any impediments in your way?
...
The daily scrum meeting is not used as a problem-solving or issue resolution meeting. Issues that are raised are taken offline and usually dealt with by the relevant subgroup immediately after the meeting.
Intro to Scrum in Under 10 Minutes
Can explain XP
The following description was adapted from the XP home page, emphasis added:
Extreme Programming (XP) stresses customer satisfaction. Instead of delivering everything you could possibly want on some date far in the future, this process delivers the software you need as you need it.
XP aims to empower developers to confidently respond to changing customer requirements, even late in the life cycle.
XP emphasizes teamwork. Managers, customers, and developers are all equal partners in a collaborative team. XP implements a simple, yet effective environment enabling teams to become highly productive. The team self-organizes around the problem to solve it as efficiently as possible.
XP aims to improve a software project in five essential ways: communication, simplicity, feedback, respect, and courage. Extreme Programmers constantly communicate with their customers and fellow programmers. They keep their design simple and clean. They get feedback by testing their software starting on day one. Every small success deepens their respect for the unique contributions of each and every team member. With this foundation, Extreme Programmers are able to courageously respond to changing requirements and technology.
XP has a set of simple rules. XP is a lot like a jig saw puzzle with many small pieces. Individually the pieces make no sense, but when combined together a complete picture can be seen. This flow chart shows how Extreme Programming's rules work together.
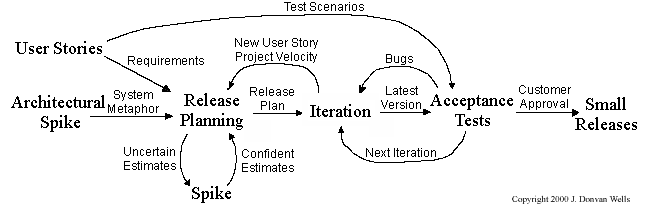
Pair programming, CRC cards, project velocity, and standup meetings are some interesting topics related to XP. Refer to extremeprogramming.org to find out more about XP.